Start, list, and cache conversations with XMTP
Most of the time, when interacting with the network, you'll want to do it through conversations. Conversations are between two wallets addresses.
Check if an address is on the network
First you need to check if the address you want to message is on the XMTP network. You can do this by calling client.canMessage with the address you want to message.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
const isOnNetwork = await client.canMessage(
"0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897",
{ env: "production" },
);
You can bulk check addresses up to 1k at the same time.
const areOnNetwork = await client.canMessage([
"address1",
"address2",
"...",
"adress1000",
]);
import { useCanMessage } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
export const CanMessage: React.FC = () => {
const [peerAddress, setPeerAddress] = useState("");
const [isOnNetwork, setIsOnNetwork] = useState(false);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const { canMessage } = useCanMessage();
const handleAddressChange = useCallback((e: React.KeyboardEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setPeerAddress(e.target.value);
}, []);
const handleCheckAddress = useCallback(async (e: FormEvent) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (isValidAddress(peerAddress)) {
setIsLoading(true);
setIsOnNetwork(await canMessage(peerAddress));
setIsLoading(false);
} else {
setIsOnNetwork(false);
}
};
void checkAddress();
}, [peerAddress]);
return (
<form onSubmit={handleCheckAddress}>
<input
name="addressInput"
type="text"
onChange={handleAddressChange}
disabled={isLoading}
/>
</form>
);
};
val canMessage = client.canMessage(bobClient.address)
let canAliceMessageBob = try await client.canMessage(bobClient.address)
val canMessage = client.canMessage(fixtures.bobClient.address)
import { Client } from "@xmtp/xmtp-react-native";
const isOnDevNetwork = await Client.canMessage(
"0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897",
);
Be sure to provide error messaging when a user enters an address in the To field and the address hasn't yet created an XMTP identity.
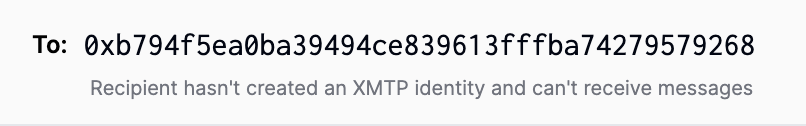
Start a new conversation
You can create a new conversation with any address activated on the XMTP network. To learn more about supported addresses, see Chains.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
const newConversation = await xmtp.conversations.newConversation(
"0x937C0d4a6294cdfa575de17382c7076b579DC176",
);
import { isValidAddress, useStartConversation } from "@xmtp/react-sdk";
import { useCallback, useState } from "react";
export const StartConversation: React.FC = () => {
const [peerAddress, setPeerAddress] = useState("");
const [message, setMessage] = useState("");
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const { startConversation } = useStartConversation();
const handleAddressChange = useCallback(
(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setPeerAddress(e.target.value);
},
[],
);
const handleMessageChange = useCallback(
(e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
setMessage(e.target.value);
},
[],
);
const handleStartConversation = useCallback(
async (e: React.FormEvent) => {
e.preventDefault();
if (peerAddress && message) {
setIsLoading(true);
const conversation = await startConversation(peerAddress, message);
setIsLoading(false);
}
},
[message, peerAddress, startConversation],
);
return (
<form onSubmit={handleStartConversation}>
<input
name="addressInput"
type="text"
onChange={handleAddressChange}
disabled={isLoading}
/>
<input
name="messageInput"
type="text"
onChange={handleMessageChange}
disabled={isLoading || !isValidAddress(peerAddress)}
/>
</form>
);
};
val newConversation =
client.conversations.newConversation("0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897")
let newConversation = try await client.conversations.newConversation(
with: "0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897")
var convo = await client.newConversation("0x...");
const newConversation = await xmtp.conversations.newConversation(
"0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897",
);
List existing conversations
You can get a list of all conversations that have one or more messages.
These conversations include all conversations for a user regardless of which app created the conversation. This functionality provides the concept of an interoperable inbox, which enables a user to access all of their conversations in any app built with XMTP.
To provide a user-friendly cold start (first load), display a "Loading conversations" status message and a progress bar.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
const allConversations = await xmtp.conversations.list();
// Say gm to everyone you've been chatting with
for (const conversation of allConversations) {
console.log(`Saying GM to ${conversation.peerAddress}`);
await conversation.send("gm");
}
export const ListConversations: React.FC = () => {
const { conversations, error, isLoading } = useConversations();
if (error) {
return "An error occurred while loading conversations";
}
if (isLoading) {
return "Loading conversations...";
}
return (
...
);
};
val allConversations = client.conversations.list()
for (conversation in allConversations) {
print("Saying GM to ${conversation.peerAddress}")
conversation.send(text = "gm")
}
let allConversations = try await client.conversations.list()
for conversation in allConversations {
print("Saying GM to \(conversation.peerAddress)")
try await conversation.send(content: "gm")
}
var conversations = await client.listConversations();
for (var convo in conversations) {
debugPrint('Saying GM to ${convo.peer}');
await client.sendMessage(convo, 'gm');
}
const allConversations = await xmtp.conversations.list();
// Say gm to everyone you've been chatting with
for (const conversation of allConversations) {
console.log(`Saying GM to ${conversation.peerAddress}`);
await conversation.send("gm");
}
Note on Group Chats
All the features and methods described in this document, including starting new conversations, checking if an address is on the network, and listing existing conversations, also apply to group chats. XMTP's approach to conversations is designed to be consistent across both one-on-one and group conversations, ensuring a seamless development experience.
For more details about building group chat specifically, refer to the Group Chat documentation.
Cache the conversation list
When running in a browser, conversations are cached in LocalStorage by default. Running client.conversations.list() will update that cache and persist the results to the browser's LocalStorage. The data stored in LocalStorage is encrypted and signed using the Keystore's identity key so that attackers cannot read the sensitive contents or tamper with them. Caching the conversation list can improve performance by up to 90%.
To disable this behavior, set the persistConversations client option to false.
- JavaScript
- React
- Kotlin
- Swift
- Dart
- React Native
const clientWithNoCache = await Client.create(signer, {
persistConversations: false,
});
const { initialize } = useClient();
const options = {
persistConversations: false,
};
await initialize({ signer, options });
val client = Client().create(signer, { env: "dev" })
val conversations = client.conversations.export()
saveConversationsSomewhere(JSON.stringify(conversations))
// To load the conversations in a new SDK instance you can run:
val client = Client.create(signer, { env: "dev" })
val conversations = JSON.parse(loadConversationsFromSomewhere())
val client.importConversation(conversations)
Serialize/Deserialize conversations: You can save a conversation object locally using its encodedContainer property. This returns a ConversationContainer object which conforms to Codable.
// Get a conversation
val conversation =
client.conversations.newConversation("0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897")
// Dump it to JSON
val gson = GsonBuilder().create()
val data = gson.toJson(conversation)
// Get it back from JSON
val containerAgain =
gson.fromJson(data.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8), ConversationV2Export::class.java)
// Get an actual Conversation object like we had above
val decodedConversation = containerAgain.decode(client)
decodedConversation.send(text = "hi")
Serialize/Deserialize conversations: You can save a conversation object locally using its encodedContainer property. This returns a ConversationContainer object which conforms to Codable.
// Get a conversation
let conversation = try await client.conversations.newConversation(
with: "0x3F11b27F323b62B159D2642964fa27C46C841897")
// Get a container.
let container = conversation.encodedContainer
// Dump it to JSON
let encoder = JSONEncoder()
let data = try encoder.encode(container)
// Get it back from JSON
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let containerAgain = try decoder.decode(ConversationContainer.self, from: data)
// Get an actual Conversation object like we had above
let decodedConversation = containerAgain.decode(with: client)
try await decodedConversation.send(text: "hi")
Code sample coming soon
Code sample coming soon

